- Found at :
 www.adafruit.com
www.adafruit.com

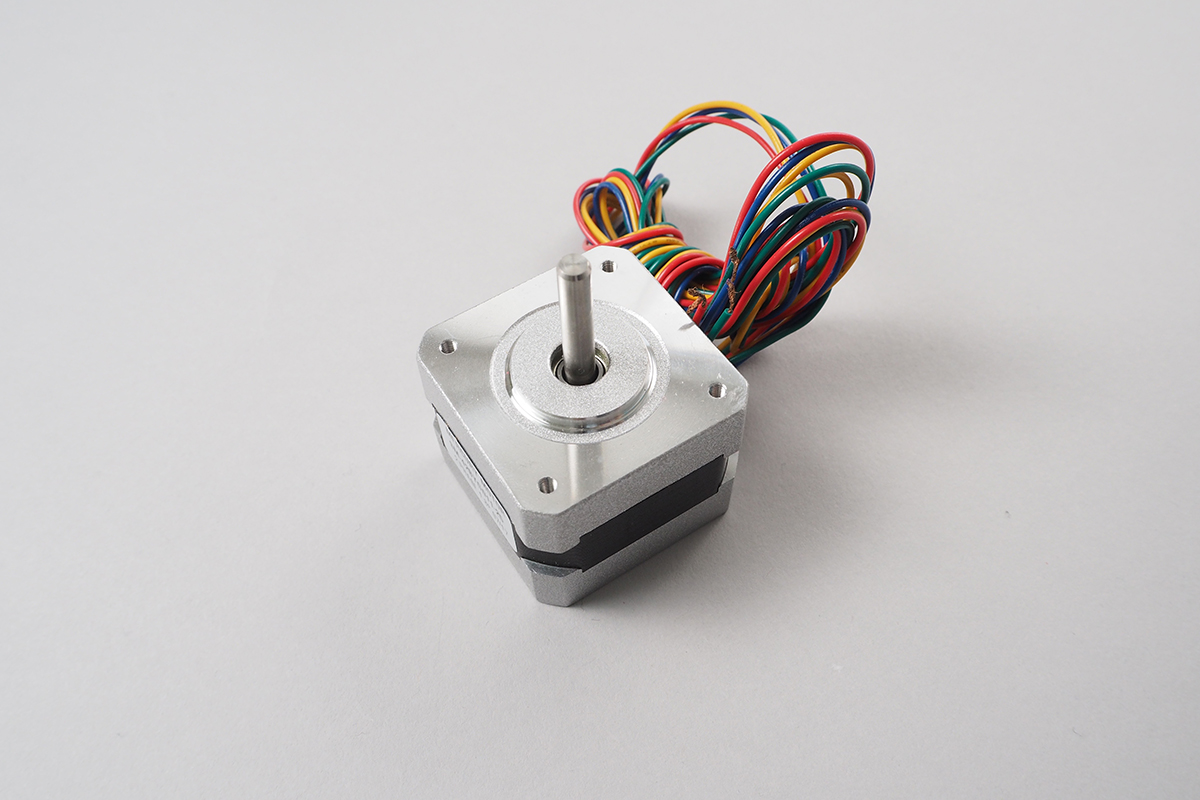
StepperMotor
Stepper Motor is different from just rotating things like DC motors.
It rotate by following electrical pulse. So, It can rotate correctly by step.
So It is very useful when you want to move/rotate things correctly, and hold something at current state. In the other hands, Stepper Motor is not good for high-speed/high-power usages.
This library can drive both bipolar/unipolar stepper motors. This cabale to drive directy from obniz Board io. So 5v stepper motor is best.


wired(obniz, {a, b, aa, bb [, common]})
It recognize connected io.
See below image to connect.

This function recognize motor bipolar/unipolar by specifying common.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | number(obniz Board io) |
no | Specify obniz Board io | |
| b | number(obniz Board io) |
no | Specify obniz Board io | |
| aa | number(obniz Board io) |
no | Specify obniz Board io. This is other side of a. | |
| bb | number(obniz Board io) |
no | Specify obniz Board io. This is other side of b. | |
| common | number(obniz Board io) |
no | Specify only when unipolar. |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.stepWait(200);
console.log(motor.currentStep); // => 300
stepType(type: string)
It change stepping method. By default, it is 2
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | string |
yes | '2' |
See below options |
| keyname | type | description |
|---|---|---|
'1' |
1 phase ecitation | Only one coil is driven. Low power consumption. But not strong |
'2' |
2 phase ecitation | Two coil is always driven. Very common. |
'1-2' |
1-2 phase ecitation | Combination of above two method. Step is 1/2. |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.stepType('1');
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.stepWait(200);
console.log(motor.currentStep); // => 300
speed(frequency: number)
It specify speed in hz. 100 means 100 step per sec.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| frequency | number |
yes | 100 |
frequency of steps |
Limit of frequency is depends on motor which you are using. High frequency has risks of slips.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.speed(1000);
await motor.stepWait(100);
[await] stepWait(step: number)
It rotate a motor by specified steps.
Also it follow speed and stepType.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| step | number |
yes | - | Steps wants to move |
If decimal number was provided, then the number will be rounded.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.stepWait(-100);
// now returned to start position.
[await] stepToWait(destination: number)
It rotate a motor to specified destionation step.
Also it follow speed and stepType.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| destination | number |
yes | - | Destionation step |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.stepToWait(-150); // it move -250 steps
console.log(motor.currentStep) // => -150
[await] holdWait()
Drain current to keep position.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.holdWait();
[await] freeWait()
Stop drain current and make free a motor.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.freeWait();
currentStep
It is current step count number. Initially 0.
When you move +100 then -50, It is 50
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
await motor.stepWait(100);
await motor.stepToWait(-150); // it move -250 steps
console.log(motor.currentStep) // => -150
[await] rotateWait(rotation: number)
It rotate by specified angle.
It also follow rotationStepCount variable. Please set correct number first.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rotation | number |
yes | - | angle to move in degree |
360 measn one rotate.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.rotationStepCount = 100;
await motor.rotateWait(360 * 2);
console.log(motor.currentRotation()); // => 720
console.log(motor.currentAngle()); // => 0
[await] rotateToWait(rotation: number)
It rotate to specified angle. (Initial angle is recognized as 0).
It rotate at minimum rotation.
It also follow rotationStepCount variable. Please set correct number first.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| angle | number |
yes | - | Destination angle in degree |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.rotationStepCount = 100;
await motor.rotateWait(355);
await motor.rotateToWait(0); // it rotate only 5
rotationStepCount
It is configration of needed step count to one rotation.
It depends on your motor. It initially 100.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.rotationStepCount = 100;
await motor.rotateToWait(90);
[await] moveWait(distance: number)
It rotate specified distance in mm.
It also follow milliMeterStepCount variable. Please set correct number first.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance | number |
yes | - | distance to be moved |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.milliMeterStepCount = 10;
await motor.moveWait(100);
await motor.moveWait(-10);
console.log(motor.currentDistance()); // => 90
[await] moveToWait(destination: number)
It rotate to specified distance in mm. Initial position is recognized as 0.
It also follow milliMeterStepCount variable. Please set correct number first.
| name | type | required | default | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| destination | number |
yes | - | destination distance in mm |
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.milliMeterStepCount = 10;
await motor.moveWait(100);
await motor.moveToWait(-10);
console.log(motor.currentDistance()); // => -10
milliMeterStepCount
It is configration of needed step count to move 1 mm.
It depends on your motor. It initially 1.
// Javascript Example
var motor = obniz.wired("StepperMotor", {a:0, aa:1, b:2, bb:3});
motor.milliMeterStepCount = 10;
await motor.moveWait(100);
await motor.moveToWait(-10);
console.log(motor.currentDistance()); // => -10
Supported from: obniz.js 3.5.0